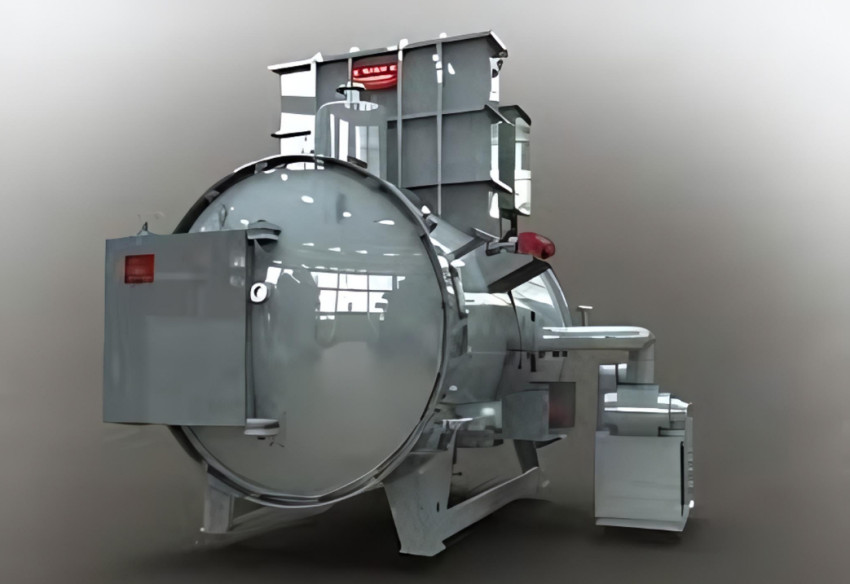
Furnaces play a crucial role in various industrial processes, especially those involving the heating or treatment of materials. Among the different types of furnaces, vacuum furnaces and atmosphere furnaces are two distinct categories, each designed for specific applications and operating environments.
Vacuum Furnace
A vacuum furnace is a specialized type of furnace that operates under low-pressure conditions, typically below atmospheric pressure. It is designed to create an environment devoid of atmospheric gases, allowing for precise control over the heating process.
Definition and Purpose
A vacuum furnace is a thermal processing unit used for heat treatment and materials processing in a controlled environment with low atmospheric pressure. The primary purpose of a vacuum furnace is to heat materials while minimizing oxidation and contamination, thus ensuring high-quality results in various industrial applications.
Operating Environment
Vacuum furnaces operate in a low-pressure environment, typically ranging from a few millibars to several torr. This low-pressure condition eliminates the presence of atmospheric gases such as oxygen and nitrogen, creating an inert atmosphere ideal for heat treatment processes.
Key Features
Absence of Atmospheric Gases
One of the defining features of a vacuum furnace is the absence of atmospheric gases inside the heating chamber. This allows for the elimination of oxidation and contamination during heating processes, resulting in cleaner and higher quality treated materials.
Control of Pressure Levels
Vacuum furnaces offer precise control over pressure levels within the heating chamber. This control enables operators to tailor the process conditions according to specific material requirements, ensuring optimal results for various applications.
Applications
Heat Treatment of Metals
Vacuum furnaces are widely used for heat treating metals, including annealing, tempering, brazing, and hardening processes. The absence of atmospheric gases prevents surface oxidation and decarburization, resulting in superior metallurgical properties and surface finishes.
Sintering Processes
Vacuum sintering is a common application of vacuum furnaces, particularly in powder metallurgy and ceramic processing industries. The controlled atmosphere and temperature conditions facilitate the densification of powdered materials, producing components with high density and mechanical strength.
Atmosphere Furnace
An atmosphere furnace, in contrast to a vacuum furnace, operates in a controlled atmosphere environment with specific gas compositions. This type of furnace is designed to accommodate various heat treatment processes while maintaining precise control over the surrounding atmosphere.
Definition and Purpose
An atmosphere furnace is a thermal processing unit equipped to operate in a controlled atmosphere environment. Its primary purpose is to heat treat materials while subjecting them to specific gas compositions, such as nitrogen, hydrogen, or carbon-containing atmospheres, to achieve desired material properties and surface finishes.
Operating Environment
Atmosphere furnaces operate in a controlled atmosphere environment, where the composition of gases surrounding the heated materials is carefully regulated. This environment allows for the implementation of specific heat treatment processes tailored to the requirements of different materials and applications.
Key Features
Presence of Controlled Atmosphere
Unlike vacuum furnaces, atmosphere furnaces maintain a controlled atmosphere within the heating chamber. The composition of gases, such as nitrogen, hydrogen, argon, or carbon-containing atmospheres, can be adjusted to suit the requirements of specific heat treatment processes.
Temperature Regulation
Atmosphere furnaces offer precise temperature control capabilities, allowing for the implementation of various heat treatment processes, including annealing, carburizing, nitriding, and brazing. The temperature profiles can be adjusted according to the material properties and desired outcomes.
Applications
Annealing
Annealing is a heat treatment process commonly performed in atmosphere furnaces to soften materials, relieve internal stresses, and improve machinability. The controlled atmosphere environment helps prevent oxidation and ensures uniform heating throughout the material.
Carburizing
Carburizing is a surface hardening process that involves introducing carbon into the surface layer of a material to improve its wear resistance. Atmosphere furnaces equipped with carbon-containing atmospheres, such as methane or propane, are used for carburizing processes in industries such as automotive and aerospace.
Comparison
When comparing vacuum furnaces and atmosphere furnaces, several key factors differentiate the two types of equipment, including environmental conditions, process control capabilities, and material suitability.
Environmental Conditions
Atmospheric Gases
Vacuum furnaces operate in a low-pressure environment devoid of atmospheric gases, while atmosphere furnaces maintain a controlled atmosphere with specific gas compositions.
Oxidation and Contamination
Vacuum furnaces eliminate the risk of oxidation and contamination by removing atmospheric gases, whereas atmosphere furnaces rely on controlled atmospheres to prevent undesired reactions during heating processes.
Process Control
Pressure Levels
Vacuum furnaces offer precise control over pressure levels within the heating chamber, allowing for tailored heat treatment processes. Atmosphere furnaces provide control over gas compositions and temperature profiles to achieve desired material properties.
Heat Treatment Processes
Vacuum furnaces are well-suited for processes requiring a clean and inert environment, such as annealing and sintering. Atmosphere furnaces are preferred for processes involving specific gas interactions, such as carburizing and nitriding.
Material Suitability
Metals and Alloys
Both vacuum furnaces and atmosphere furnaces are suitable for heat treating metals and alloys. Vacuum furnaces are preferred for materials sensitive to oxidation, while atmosphere furnaces offer versatility for introducing specific gas elements into the material surface.
Ceramics and Composites
Vacuum furnaces are commonly used for sintering ceramic powders and processing composite materials due to their inert environment. Atmosphere furnaces can also be adapted for ceramic processing with tailored gas compositions.
Are you ready to buy this product? It’s easy to purchase by visiting our product page!
Conclusion
In conclusion, vacuum furnaces and atmosphere furnaces serve distinct purposes in thermal processing applications, offering unique advantages and capabilities. Understanding the differences between these two types of furnaces is essential for selecting the most suitable equipment for specific material requirements and heat treatment processes.
Vacuum furnaces operate in a low-pressure environment devoid of atmospheric gases, while atmosphere furnaces maintain a controlled atmosphere with specific gas compositions. Vacuum furnaces are preferred for processes requiring a clean and inert environment, such as annealing and sintering, while atmosphere furnaces offer versatility for processes involving specific gas interactions, such as carburizing and nitriding.
When selecting between vacuum furnaces and atmosphere furnaces, factors such as material sensitivity to oxidation, desired heat treatment processes, and required material properties should be considered. Vacuum furnaces are ideal for materials prone to oxidation, while atmosphere furnaces offer flexibility for introducing specific gas elements into the material surface. Ultimately, the choice of furnace type depends on the specific requirements of the application and desired outcomes.