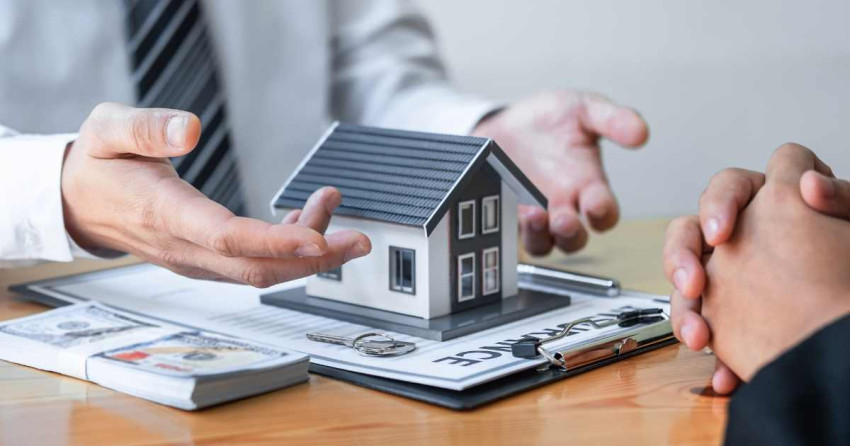
When availing a loan against property, legal documentation plays a crucial role in ensuring that the transaction is legally secure and protects the rights of both the borrower and the lender. Legal documents serve as evidence of the loan agreement, terms, and conditions, and provide a record of the property being pledged as collateral. In this article, we will explore the significance of legal documentation in the loan against property process and the key documents involved.
Importance of Legal Documentation
Legal documentation is essential in a loan against property for several reasons:
Legally binding agreement: The loan agreement, which is a legally binding contract between the borrower and lender, outlines the terms and conditions of the loan. It includes details such as the loan amount, interest rate, repayment schedule, and penalties for defaulting. Legal documentation ensures that both parties are aware of their rights and obligations, reducing the risk of misunderstandings or disputes in the future.
Protecting the rights of the lender: The legal documentation, such as the mortgage deed or property charge, serves as collateral for the lender. It provides the lender with a legal claim on the property in case the borrower defaults on the loan. The mortgage deed establishes the lender's right to seize and sell the property to recover the outstanding dues. This documentation protects the lender's financial interests and helps ensure repayment.
Ensuring title and property ownership: Legal documentation includes property-related documents such as the sale deed, title deed, and encumbrance certificate. These documents establish the ownership of the property and ensure that it is free from any legal disputes or encumbrances. Lenders require these documents to verify the legal ownership and marketability of the property being pledged as collateral.
Complying with legal regulations: Legal documentation in a loan against property is important to comply with various legal and regulatory requirements. These may include documentation related to income proof, KYC (Know Your Customer) documents, property valuation reports, and other documents mandated by the lender or regulatory authorities. Complying with legal regulations ensures that the loan transaction is carried out in adherence to the law.
Key Legal Documents Involved
Several legal documents are involved in a loan against property. The specific documents required may vary based on the lender's policies and the borrower's profile. Here are some of the key legal documents typically involved in the process:
Loan Agreement: The loan agreement is the primary legal document that outlines the terms and conditions of the loan. It includes details such as the loan amount, interest rate, repayment schedule, and other clauses. Both the borrower and the lender must carefully review and sign the loan agreement, acknowledging their acceptance of the terms and conditions.
Mortgage Deed or Property Charge: The mortgage deed is a legal document that creates a charge on the property being pledged as collateral. It establishes the lender's right over the property in case of loan default. It should contain all relevant information about the property, including its description, location, boundaries, and encumbrances. The mortgage deed is typically registered with the appropriate land registry or authority.
Sale Deed or Title Deed: The sale deed or title deed is a legal document that establishes the ownership of the property. It contains details of the property's transfer from the previous owner to the borrower. The lender may require a copy of the sale deed or title deed to verify the property's ownership before approving the loan.
Encumbrance Certificate: An encumbrance certificate is a document issued by the Sub-Registrar's office that certifies that the property is free from any encumbrances or liabilities. It confirms that there are no pending loans, mortgages, or legal claims on the property. Lenders typically require an encumbrance certificate to verify the property's marketability and ensure a clear title.
KYC Documents: Know Your Customer (KYC) documents are required by lenders to verify the borrower's identity, address, and other personal details. These documents typically include a valid identification proof (such as a passport or Aadhaar card), address proof, and photographs. KYC documentation is essential to comply with regulatory requirements and prevent fraudulent activities.
Income Proof and Financial Statements: Lenders may require income proof and financial statements, such as salary slips, bank statements, income tax returns, or audited financial statements (for self-employed individuals or businesses). These documents establish the borrower's income and repayment capacity, helping the lender assess the loan eligibility.
Property Valuation Report: A property valuation report is prepared by a qualified valuer to assess the property's market value. The report includes details of the property's physical condition, location, amenities, and the prevailing market rates. This document helps the lender determine the loan amount that can be sanctioned against the property.
FAQs
1. What happens to the legal documents after the loan is repaid?
Once the loan against property is repaid in full, the lender typically returns the original legal documents, such as the mortgage deed or property charge, to the borrower. It is advisable to keep these documents safely as proof of the closure of the loan and the release of the property's charge.
2. Can a loan against property be transferred to another person?
In some cases, it is possible to transfer a loan against property to another person. However, this process may involve certain conditions and approvals from the lender. It is essential to consult with the lender and understand the transfer process and any associated fees or charges.
3. Can legal documentation be done electronically or does it require physical copies?
In many cases, legal documentation for a loan against property can be done electronically using digital signatures and online platforms. However, some lenders may still require physical copies of certain documents. It is important to check with the lender regarding their preferred mode of documentation.
4. What is the role of a notary in the loan against property process?
A notary plays an important role in the loan against property process by authenticating certain legal documents. Notarization involves verifying the identity of the signatories and ensuring that the documents are properly executed. Some documents, such as the loan agreement or mortgage deed, may require notarization for added legal validity.
5. Can a loan against property be availed on jointly owned property?
Yes, a loan against property can be availed on a jointly owned property. In such cases, all co-owners of the property will need to sign the legal documents as borrowers or guarantors, depending on their involvement in the loan agreement. The ownership shares of each co-owner will be considered while determining the loan amount and liability.
In conclusion, legal documentation plays a pivotal role in the loan against property process. It ensures a legally secure transaction, protects the rights of both the borrower and the lender, and establishes the ownership and marketability of the property. It is essential for borrowers to understand the importance of legal documentation and ensure that all necessary documents are prepared, verified, and executed correctly to facilitate a smooth loan transaction.