In today's world of flexible work arrangements and private offices, the importance of strong security services has become increasingly important. Ensuring the safety and confidentiality of sensitive information is crucial for businesses and individuals alike. In this blog, we will explore a comprehensive guide to security measures tailored for private workspaces, offering insights into creating a secure and protected environment.
Access Control Systems:
At the heart of private workspace security lies effective access control. Implementing access control systems ensures that only authorized individuals can enter designated areas. This can include key card access, biometric identification, or keypad entry systems. By restricting access to specific personnel, businesses can safeguard sensitive information against unauthorized entry.
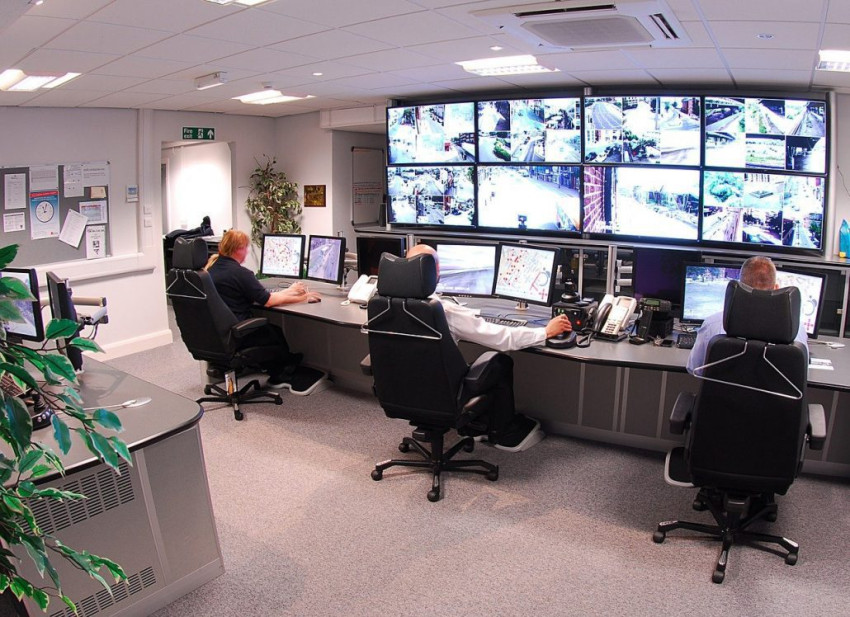
Surveillance Cameras:
Strategic placement of surveillance cameras is an essential aspect of private workspace security. Cameras act both as a deterrent and a tool for live monitoring and recording activities. High-resolution cameras placed at entry points, common areas, and sensitive zones provide a visual record that can be invaluable in identifying and addressing security incidents.
Alarm Systems:
Incorporating alarm systems adds an additional layer of security to private workspaces. Modern alarm systems can detect unauthorized access, motion, or even environmental changes such as smoke or fire. When triggered, these systems can alert the security team, law enforcement, or designated individuals, ensuring a swift response to potential security threats.
Physical Security Measures:
Beyond electronic systems, physical security measures play a crucial role in office security in Calgary. This includes reinforced doors and windows, security grilles, and strong locks. Putting strong physical barriers can deter unauthorized access and provide an extra layer of protection against break-ins.
Cybersecurity Protocols:
In an era where digital information is as valuable as physical assets, cybersecurity is a necessary component of private workspace security. Implementing strong password policies, encrypting sensitive data, and regularly updating security software are essential measures to protect against cyber threats. Educating employees on cybersecurity best practices is equally important in maintaining a secure digital environment.
Employee Training and Awareness:
Human factors contribute significantly to workspace security. Training employees on security protocols, emergency procedures, and the importance of confidentiality fosters a security-conscious culture. Regular awareness programs and updates ensure that everyone in the workspace remains vigilant and understands their role in maintaining a secure environment.
Secure Document Management:
Implementing secure document management systems is important for private workspaces dealing with confidential documents. This includes secure filing cabinets, access restrictions to document storage areas, and policies for properly disposing of sensitive materials. Maintaining control over physical documents is as important as securing digital data.
Emergency Response Plans:
Preparing for emergencies is a key component of workspace security. Developing and practicing emergency response plans, including evacuation procedures and communication protocols, ensures that security guards are well-prepared to respond effectively in the event of a security threat, natural disaster, or other emergencies.
Visitor Management Systems:
Effectively managing and monitoring visitor access is crucial for private workspaces. Implementing visitor management systems, which may include sign-in procedures, visitor badges, and escort policies, helps control access and ensures that only authorized individuals are present within the workspace.
Regular Security Audits and Updates:
Security is an evolving landscape, and it is essential to conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and areas for improvement. This includes assessing the effectiveness of existing security measures, updating systems as needed, and staying informed about the latest security technologies and best practices.
Conclusion:
Keeping private workspaces safe involves various aspects that require a combination of physical, electronic, and procedural measures. By incorporating access control systems, surveillance cameras, alarm systems, physical security measures, cybersecurity protocols, employee training, secure document management, emergency response plans, visitor management systems, and regular security audits, businesses can create a comprehensive and effective security framework. A secure private workspace not only protects valuable assets but also instills confidence among employees and stakeholders, fostering a productive and protected work environment.