Asthma, a chronic respiratory condition affecting millions worldwide, has long been associated with environmental triggers and genetic predisposition. However, recent research has sparked interest in the potential autoimmune aspects of asthma. Let's delve into the intricate relationship between asthma and the immune system.
Understanding Asthma
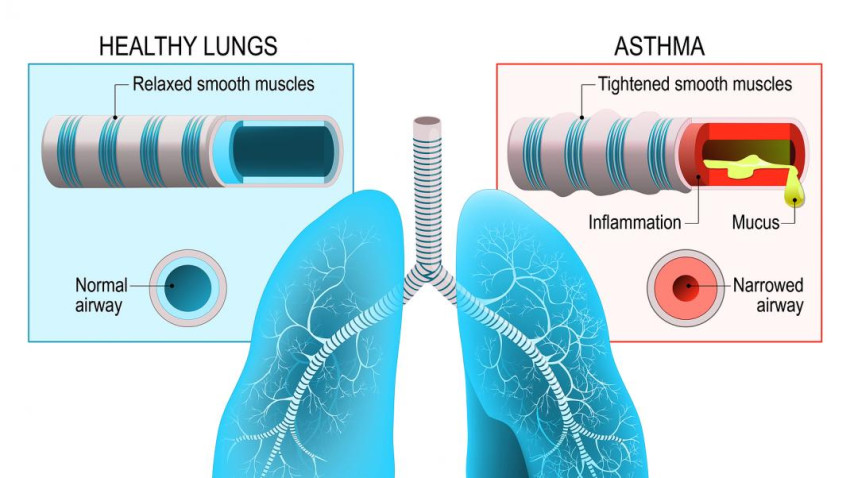
Asthma is characterized by inflammation of the airways, leading to symptoms such as wheezing, shortness of breath, chest tightness, and coughing. Traditionally, asthma has been considered an allergic or hypersensitivity disorder, with environmental factors triggering immune responses that cause airway inflammation.
The Immune System's Role
The immune system, a complex network of cells and proteins, is our body's defense against invaders. In asthma, the immune system's response goes awry, leading to inflammation and heightened sensitivity in the airways. This response is commonly triggered by allergens like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander.
Autoimmune Paradigm:
While asthma has primarily been viewed through the lens of allergic reactions, recent studies suggest that autoimmune mechanisms might also play a role. In autoimmune conditions, the immune system mistakenly targets and attacks the body's tissues. Although asthma is not classified as a classic autoimmune disease, there are intriguing connections.
Shared Immunological Features:
Certain autoimmune diseases and asthma share common immunological features. Both involve dysregulation of T-helper cells, cytokines, and other immune components. This has led researchers to explore whether asthma, in some cases, may involve an autoimmune component, where the immune system mistakenly identifies the body's own cells as threats.
Autoimmune Markers in Asthma:
Studies have identified autoimmune markers in individuals with asthma. Autoantibodies, which are antibodies that target the body's tissues, have been found in the lungs of some asthma patients. This discovery raises questions about whether the immune system's attack on lung tissues contributes to asthma symptoms.
Genetic Links:
Genetics also play a role in both autoimmune diseases and asthma. Certain genetic factors associated with autoimmune conditions have been found to influence asthma susceptibility. This genetic overlap suggests shared underlying mechanisms.
Environmental Triggers and Autoimmunity
Environmental factors known to trigger asthma, such as pollution and respiratory infections, have also been linked to the development or exacerbation of autoimmune diseases. This intersection raises intriguing possibilities regarding the intricate interplay between environmental triggers, the immune system, and asthma.
Clinical Implications
Recognizing potential autoimmune aspects of asthma has significant clinical implications. It may pave the way for personalized treatment approaches that target specific immune pathways. Immunomodulatory therapies, commonly used in autoimmune conditions, could be explored as potential interventions for certain asthma subtypes.
Challenges and Questions
While the autoimmune connection in asthma is a fascinating area of research, challenges and unanswered questions remain. It's essential to note that not all cases of asthma involve autoimmune mechanisms, and the relationship is likely complex and multifaceted.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the evolving understanding of asthma's immunological landscape opens new avenues for research and treatment. While asthma has long been viewed as primarily allergic, the potential autoimmune connection adds nuance to our comprehension of this complex respiratory condition. Unraveling the intricacies of asthma's relationship with the immune system could pave the way for more targeted and effective therapies, offering hope for better management and improved quality of life for individuals living with asthma.




