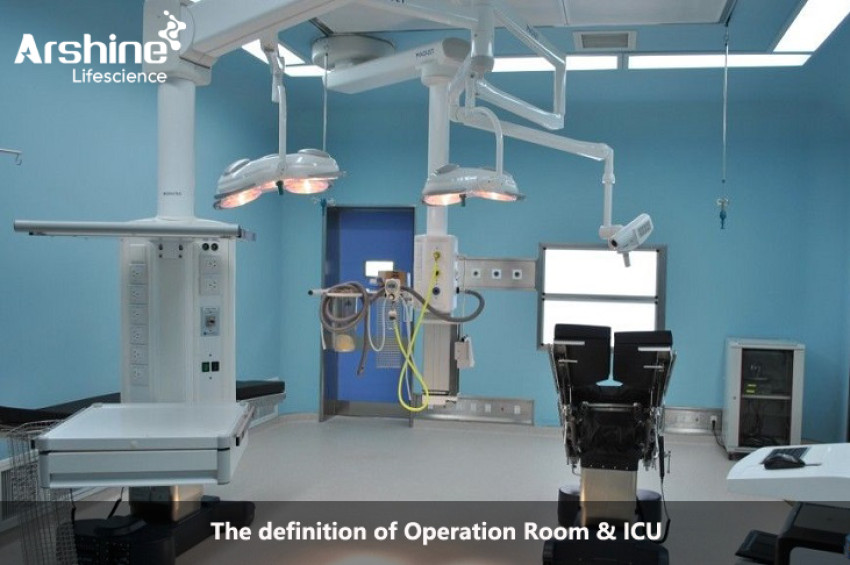
The Operating Room (OR):
The operating room, often referred to as the OR, is a critical area within a hospital or medical facility where surgical procedures are performed. It is a highly specialized and controlled environment designed to provide a safe and sterile setting for surgical teams to carry out various medical interventions. The OR plays a pivotal role in the continuum of patient care, as it is where many life-saving and complex surgeries take place.
Components of the Operating Room:
The operating room is a complex space with various components that contribute to its functionality and safety. Some of the key components include:
Surgical Team: The surgical team is a group of highly skilled medical professionals, including surgeons, anesthesiologists, nurses, surgical technicians, and other support staff, all working together to ensure the success of the surgical procedure.
Sterile Environment: Maintaining a sterile environment is paramount in the OR to prevent infections and complications. All personnel entering the OR must adhere to strict protocols, including wearing sterile attire and following proper handwashing procedures.
Surgical Table: The surgical table is a specialized platform where the patient lies during the procedure. It is designed to be adjustable and positionable to provide optimal access for the surgical team.
Anesthesia System: Anesthesia is administered to the patient to induce unconsciousness and manage pain during surgery. An anesthesia machine and various monitoring devices are used to deliver and monitor anesthesia throughout the procedure.
Surgical Equipment: The OR is equipped with a wide range of specialized surgical instruments and equipment specific to different procedures, such as scalpels, forceps, retractors, and electrosurgical devices.
Imaging and Visualization Technology: Modern ORs often have advanced imaging and visualization technology, such as X-ray machines, fluoroscopy, endoscopy, and laparoscopic equipment, which aid surgeons in performing minimally invasive procedures.
Environmental Controls: The OR maintains strict environmental controls, including temperature, humidity, and air filtration, to ensure optimal conditions for surgery and prevent infections.
Surgical Lights: Bright, adjustable surgical lights are essential for providing adequate illumination of the surgical field, enabling surgeons to perform precise maneuvers.
Communication Systems: Effective communication is vital in the OR. Intercoms and audiovisual equipment allow the surgical team to communicate with each other and seek consultations with experts outside the OR when needed.
The Role of the Operating Room in Healthcare:
The operating room serves as a crucial component of the healthcare system, providing a controlled and safe environment for various surgical interventions. It plays a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes by facilitating the following:
Life-Saving Procedures: The OR is where emergency surgeries, such as trauma interventions and organ transplants, are performed, often saving patients' lives.
Elective Surgeries: Many elective procedures, such as joint replacements, cardiac surgeries, and tumor removals, are carried out in the OR to improve patients' quality of life and alleviate pain.
Diagnostics and Therapeutics: In some cases, exploratory surgeries are performed to diagnose and determine the extent of certain medical conditions. Additionally, surgeries may be therapeutic, removing tumors or correcting abnormalities.
Minimally Invasive Techniques: The OR is a hub for innovative minimally invasive techniques, such as laparoscopy and robotic-assisted surgery, which reduce patient trauma, minimize scarring, and accelerate recovery times.
Research and Education: The OR often serves as a platform for medical research and education. Surgeons may utilize it to train medical students and residents, as well as to explore and refine new surgical techniques.
Multi-Disciplinary Collaboration: Complex cases often require input from various medical specialties. The OR allows surgeons, specialists, and other healthcare professionals to collaborate in real-time to optimize patient care.
Sterile Procedures and Infection Control:
One of the primary goals of the OR is to maintain a sterile environment to minimize the risk of surgical site infections (SSIs). SSIs can lead to significant complications, prolonged hospital stays, and increased healthcare costs. To ensure infection control, the following practices are meticulously followed:
Surgical Attire and Hand Hygiene: All OR personnel, including surgeons, nurses, and technicians, must wear sterile gowns, gloves, masks, and caps. They also perform thorough handwashing and use surgical hand scrubs before entering the OR.
Surgical Site Preparation: The patient's surgical site is prepared and sterilized using antiseptic solutions to minimize the presence of bacteria on the skin.
Aseptic Technique: The surgical team uses aseptic techniques during the entire procedure, ensuring that sterile instruments and equipment are handled appropriately and that the surgical field is maintained free of contamination.
Sterile Instrumentation and Supplies: All surgical instruments, drapes, and supplies used in the OR are carefully sterilized using methods such as autoclaving or chemical disinfection before use.
Air Quality and Filtration: The OR's ventilation system includes high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters to reduce airborne particles, bacteria, and viruses, helping maintain a clean environment.
Traffic Control and Restricted Access: The OR restricts access to authorized personnel only and enforces strict traffic control to minimize the potential for contamination.
ICU - Intensive Care Unit:
The Intensive Care Unit (ICU) is a specialized department in a hospital that provides critical care and continuous monitoring to patients with severe, life-threatening conditions. It is also known as the critical care unit or intensive therapy unit. The ICU is staffed with a highly trained team of healthcare professionals who are experienced in managing critically ill patients and using advanced medical equipment to provide essential support and interventions.
Types of Intensive Care Units:
There are various types of ICUs within a hospital, each catering to specific medical needs:
Medical ICU (MICU): MICUs focus on providing intensive care for patients with severe medical conditions, such as respiratory failure, sepsis, heart failure, and organ dysfunction.
Surgical ICU (SICU): SICUs are dedicated to caring for postoperative patients who require critical care after undergoing complex surgical procedures.
Cardiac ICU (CICU): CICUs specialize in managing patients with severe cardiac conditions, such as heart attacks, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Neonatal ICU (NICU): NICUs are designed to provide specialized care for premature infants and newborns with critical medical conditions.
Pediatric ICU (PICU): PICUs focus on caring for critically ill children and adolescents, including those with severe infections, traumatic injuries, or chronic medical conditions.
Characteristics of the ICU:
ICUs possess unique characteristics that distinguish them from other hospital departments:
High-Level Monitoring: ICU patients are continuously monitored using advanced medical equipment, such as cardiac monitors, ventilators, pulse oximeters, and intravenous infusion pumps. This constant monitoring allows healthcare providers to promptly address any changes in the patient's condition.
Close Patient Observation: ICU staff conduct frequent patient assessments, closely monitoring vital signs, neurological status, and response to treatment. Minute changes can have significant implications in the critically ill, necessitating immediate intervention.
Specialized Medical Equipment: ICUs are equipped with a wide range of specialized medical devices and equipment to support critical patients, including mechanical ventilators, hemodynamic monitoring systems, renal replacement therapy machines, and more.
Trained ICU Staff: The ICU team consists of experienced and highly trained professionals, including critical care physicians, nurses, respiratory therapists, pharmacists, and other specialists, all working collaboratively to provide comprehensive care.
Family Support: Recognizing the emotional toll on patients and their families, ICUs often have designated areas for family members to receive updates and support from the medical team.
Round-the-Clock Care: The ICU operates 24/7 to ensure continuous care and prompt response to any emergencies that may arise.
The Role of the ICU in Healthcare:
ICUs play a critical role in the healthcare system by providing specialized care for patients with severe and life-threatening conditions. Some key roles of the ICU include:
Life Support and Stabilization: The ICU serves as a bridge for patients in critical condition, providing life-saving interventions and stabilizing them until their condition improves or a definitive treatment plan is established.
Postoperative Care: After complex surgical procedures, patients may be transferred to the ICU for close monitoring and immediate management of any postoperative complications.
Management of Complex Conditions: ICUs care for patients with a wide range of medical conditions, such as sepsis, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), multiple organ failure, and severe trauma.
Ventilator Support: Patients with respiratory failure often require mechanical ventilation. The ICU staff are proficient in managing ventilators and optimizing respiratory support.
Hemodynamic Monitoring: In cases of shock or cardiovascular instability, hemodynamic monitoring techniques are used to assess blood pressure, heart function, and fluid status.
Nutritional Support: Many critically ill patients are unable to eat normally, requiring specialized nutritional support, such as enteral or parenteral feeding.
Pain Management and Sedation: Patients in the ICU may require pain management and sedation to keep them comfortable and reduce anxiety.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations:
The ICU environment presents various challenges and ethical considerations due to the complexity and severity of patients' conditions:
Resource Allocation: ICU beds and resources are often limited. Healthcare providers must make challenging decisions regarding patient prioritization and resource allocation.
End-of-Life Care: In the ICU, difficult decisions regarding end-of-life care and withdrawal of life support may arise. Healthcare providers work closely with patients and families to ensure appropriate and compassionate care.
Compassion Fatigue: Providing care in the ICU can be emotionally taxing for healthcare professionals, leading to compassion fatigue and burnout. Institutions must implement strategies to support the well-being of ICU staff.
Family Communication: Communicating with families about a critically ill patient's condition and prognosis requires sensitivity and empathy.
Advance Care Planning: Encouraging advance care planning and discussions about patients' treatment preferences can assist in making decisions aligned with their wishes.
In conclusion, the Operating Room and Intensive Care Unit are two vital components of modern healthcare, each playing a unique and indispensable role in the treatment and care of patients. The Operating Room provides a controlled and sterile environment for surgical procedures, while the ICU offers critical care and continuous monitoring for patients with severe medical conditions. Both settings are staffed with highly trained professionals who work tirelessly to ensure patient safety and optimal outcomes. The fields of surgery and critical care continue to evolve with advancements in medical technology and research, further enhancing their ability to save lives and improve patient well-being.
https://www.arshinemedical.com/Industry-information/the-definition-of-operation-room--icu




